Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kim, B. K.*; Tan, L.*; Sakasegawa, Hideo; Parish, C. M.*; Zhong, W.*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu*; Kato, Yutai*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 545, p.152634_1 - 152634_12, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kasahara, Shigeki; Fukuya, Koji*; Fujimoto, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*; Chimi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Review 2018-013, 171 Pages, 2019/01
For structural integrity assessment of reactor internals of light water reactors, it is important to evaluate and predict the property changes of structural materials, based on existing data obtained from austenitic stainless steel irradiated with neutrons. Compilation of the data into tables is valuable for discussing the representative or the most probable values of the properties applied to the assessment. When the data compilation, the data must be distinguished clearly in consideration of different service conditions of core internals of pressurized water reactors (PWR) and boiling water reactors. Main objective of this work is to provide material property tables of irradiated austenitic stainless steel which will be applicable for assessment of structural integrity of core internals of PWRs. To compile the table, published literature reporting irradiated stainless steel data were surveyed and screened by considering the service conditions of PWRs. In addition to the data, various parameters for the data evaluation, e.g. chemical compositions and pre-treatments of the materials, irradiation and examination conditions, were extracted from the literature, and listed into tables.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Fukuya, Koji*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*; Chimi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Review 2018-012, 180 Pages, 2018/11
For structural integrity assessment of reactor internals of light water reactors, it is important to evaluate and predict the property changes of structural materials, based on existing data obtained from austenitic stainless steel irradiated with neutrons. Compilation of the data into tables is valuable for discussing the representative or the most probable values of the properties applied to the assessment. In the process of the data compilation, the data must be distinguished clearly in consideration of different service conditions of core internals of boiling water reactors (BWR) and pressurized water reactors. Main objective of this work is to provide material property tables of irradiated austenitic stainless steel which will be applicable for assessment of structural integrity of core internals of BWRs. To compile the table, published literature reporting irradiated stainless steel data were surveyed and screened by considering the service conditions of BWRs. In addition to the data, various parameters for the data evaluation, e.g. chemical compositions and pre-treatments of the materials, irradiation and examination conditions, were extracted from the literature, and listed into the tables.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Tsuru, Tomohito; Hasegawa, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 505, p.15 - 21, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:86.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tungsten (W) is considered as a promising candidate for plasma-facing materials for future nuclear fusion devices, and selecting optimal alloying constituents is a critical issue to improve radiation resistance of the W alloys as well as to improve their mechanical properties. We conducted in the current study a series of first-principles calculations for investigating solvent-solute mixed dumbbells in W crystals. The results suggested that titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), and chromium (Cr) are favorable as solutes for W alloys from irradiation-effect perspectives because these elements are expected to promote vacancy-interstitial recombination without causing radiation-induced precipitation that reduces ductility of irradiated materials.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2016-025, 101 Pages, 2016/12
The JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator complex has been used in various research fields such as nuclear science and material science by researchers not only of JAEA but also from universities, research institutes and industrial companies. This annual report covers developments of accelerators and research activities carried out using the tandem accelerator and superconducting booster from April 1, 2013 to March 31, 2014. Thirty-one summary reports were categorized into seven research/development fields:(1) accelerator operation and development, (2) nuclear structure, (3) nuclear reaction, (4) nuclear chemistry, (5) nuclear theory, (6) atomic physics and solid state physics (7) radiation effects in materials. This report also lists publications, meetings, personnel, committee members, cooperative researches and common use programs.
 Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiation
Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiationKojima, Hiroshi*; Yoshizaki, Hiroaki*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Saito, Yuichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 372, p.72 - 77, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au
Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni
ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni Al and Ni
Al and Ni V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.
V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.
Oya, Yasuhisa*; Li, X.*; Sato, Misaki*; Yuyama, Kenta*; Oyaizu, Makoto; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.402 - 405, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)The deuterium (D) permeation behaviors for ion damaged tungsten (W) by 3 keV D
 and 10 keV C
and 10 keV C were studied. The D permeability was obtained for un-damaged W at various temperatures. For both D
were studied. The D permeability was obtained for un-damaged W at various temperatures. For both D
 and C
and C implanted W, the permeability was clearly reduced. But, for the D
implanted W, the permeability was clearly reduced. But, for the D
 implanted W, the permeability was recovered by heating at 1173 K and it was almost consistent with that for un-damaged W. In the case of C
implanted W, the permeability was recovered by heating at 1173 K and it was almost consistent with that for un-damaged W. In the case of C implanted W, the permeability was not recovered even if the sample was heated at 1173 K, indicating that the existence of carbon would prevent the recovery of permeation path in W. In addition, TEM observation showed the voids were grown by heating at 1173 K and not removed, showing the existence of damages would not largely influence on the hydrogen permeation behavior in W in the present study.
implanted W, the permeability was not recovered even if the sample was heated at 1173 K, indicating that the existence of carbon would prevent the recovery of permeation path in W. In addition, TEM observation showed the voids were grown by heating at 1173 K and not removed, showing the existence of damages would not largely influence on the hydrogen permeation behavior in W in the present study.
Oshima, Takeshi; Yokoseki, Takashi; Murata, Koichi; Matsuda, Takuma; Mitomo, Satoshi; Abe, Hiroshi; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Hijikata, Yasuto*; Tanaka, Yuki*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(1S), p.01AD01_1 - 01AD01_4, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54.92(Physics, Applied)Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sato, Shinichiro; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Mochizuki, Toru*; Okano, Yoshinobu*; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.73 - 76, 2015/11
The radiation effect on GaAs p-i-n solar cells with quantum dot (QD) in the i-layer was investigated. In a previous work, we particularly noted the degradation of fill-factor (FF) for the QD cells. In this work, to clarify the reason of the FF degradation in QD cells, generation current due to low-energy proton irradiation, which we call ion beam induced current (IBIC), was observed to characterize behavior of the generated minority carrier by the protons in the depletion region where QDs are located. The energy of protons was adjusted to damage the depletion region, and decrease of generation current was measured during the proton irradiation. The results suggest that the serious degradation of FF is caused by a decrease of the carrier collection efficiency in the depletion region due to proton damage.
Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 73, 2015/03
Using a collimating heavy-ion microbeam system, we have explored various effects of heavy-ion hit on biological materials. However, there are limitations of the collimating system in the size of the microbeam spot and in the irradiation speed that cannot be overcome in principle. Thus, we started the development of a focusing microbeam system for target-irradiating individual cells more precisely. In this year, we established the protocol for irradiating "actual" cell sample with scanned beam. In the experiment, the HeLa cells were inoculated on a CR-39 film, then place on the sample stage. The microscopic image of cells was analyzed, and the cells were irradiated with scanned neon microbeam. After irradiation, we found the correspondence of the distribution pattern of the ion hit positions and the  -H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
-H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
 C and
C and  He
HeAkeo, Kiyoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Akeo, Yoko*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 80, 2015/03
It is known that superoxide dismutases (SOD) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the dismutation of superoxide into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Ionizing radiation is known to induce oxidative stress through generation of reactive oxygen species resulting in imbalance of the pro-oxidant and antioxidant in the cells, which is suggested to culminate in cell death. Therefore, we measured the activity of SOD in human RE cells exposed to the He- and C-ion beam. The cells collected at 0, 4, 8, and 24 hr after irradiation were extracted by adding the SOD assay buffer to the pellets, and lysed by several cycles of freezing and thawing. The activity of SOD was measured using a modification of the luminol assay. SOD activity decreased according to duration time after irradiation of He-ion, however, in case of C-ion, it increased at 24 hr after irradiation. The result suggested that that there were the differences of the effects by irradiation on SOD activity between He- and C-ion.
Ueda, Daisuke*; Shirai, Koji*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 84, 2015/03
In this study, we investigated the effects of irradiation to the silkworm eggs at various developmental stages. First, we tried the irradiation to the unfertilized eggs (at 1.5 hour after oviposition). At this stage, the female pronucleus and the sperm nucleus are observed in the eggs, but not fertilized. After irradiation, the irradiated eggs stopped the development after fertilization. About 2 hours after, the egg restarted the nuclear cleavage. This result indicates the DNA damage on pronuleus cannot prevent the fertilization. We also investigated the effects of irradiation to the egg at the nuclear cleavage stage (at 6 hour after oviposition). The egg also stopped the development after irradiation, but the duration time of the developmental arrest was almost two times longer (about 4 hours) than that of the egg irradiated at fertilization.
Kitabatake, Satomi*; Ushiroda, Tota*; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Okahata, Yoshio*; Ito, Atsushi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 86, 2015/03
Biological effects of high-LET radiation could be understood in terms of the ion track structure. Therefore the evaluation of the contribution of both core and penumbra regions to biological effects is an important issue for the study of high-LET effects. In the present study, we developed a protocol to make a uniform DNA sheet with insoluble nature in aqueous solution, and explored the applicability to the detection of 8-OHdG distributions after heavy-ion irradiation. Water-insoluble DNA sheet was irradiated with proton and neon ion beams at JAEA-Takasaki. After irradiation DNA samples were incubated with an 8-OHdG antibody followed by with a second antibody containing a fluorescence probe. The preliminary results indicated that upon ion irradiation randomly distributed dot-like fluorescence was observed, suggesting that these dots may be from incident ions.
Abderrahmane, A.*; Ko, P. J.*; Okada, Hiroshi*; Sato, Shinichiro; Oshima, Takeshi; Sandhu, A.*
IEEE Electron Device Letters, 35(11), p.1130 - 1132, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:49.28(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The longitudinal and transverse magnetoresistances of AlGaN/GaN heterostructure-based micro-Hall sensors were compared with samples irradiated with protons with an energy of 380 keV and fluence of 10 (protons/cm
(protons/cm ). Increases in the elastic and inelastic scattering were deduced from weak localization behavior in both samples. The AlGaN/GaN micro-Hall sensors showed stable magnetic sensitivity in non and irradiated samples and increased resistivity after proton irradiation yielded an enhanced magnetoresistance sensitivity in nonirradiated sensors from 160 to 417 V/(A
). Increases in the elastic and inelastic scattering were deduced from weak localization behavior in both samples. The AlGaN/GaN micro-Hall sensors showed stable magnetic sensitivity in non and irradiated samples and increased resistivity after proton irradiation yielded an enhanced magnetoresistance sensitivity in nonirradiated sensors from 160 to 417 V/(A  T). The minimum detectable magnetic field of irradiated micro-Hall sensors determined from magneto-voltage measurements at 4 K was similar to the minimum detectable magnetic field in the nonirradiated sensors.
T). The minimum detectable magnetic field of irradiated micro-Hall sensors determined from magneto-voltage measurements at 4 K was similar to the minimum detectable magnetic field in the nonirradiated sensors.
Hubbard, S.*; Sato, Shinichiro; Schmieder, K.*; Strong, W.*; Forbes, D.*; Bailey, C. G.*; Hoheisel, R.*; Walters, R. J.*
Proceedings of 40th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-40) (CD-ROM), p.1045 - 1050, 2014/06
Baseline and quantum dot (QD) GaAs pn-junction diodes were characterized by deep level transient spectroscopy before and after both 1MeV electron irradiation and 140 keV proton irradiation. Prior to irradiation, the addition of quantum dots appeared to have introduced a higher density of defects at EC-0.75 eV. After 1 MeV electron irradiation the well-known electron defects E3, E4 and E5 were observed in the baseline sample. In the quantum dot sample after 1 MeV electron irradiation, defects near E3, E4 and EC-0.75 eV were also observed. Compared to the irradiated baseline, the QD sample shows a higher density of more complex E4 defect and a lower density of the simple E3 defect, while the EC-0.75 eV defect seemed to be unaffected by electron irradiation. As well, after proton irradiation, well known proton defects PR1, PR2, PR4' are observed. The QD sample shows a lower density PR4' defects and a similar density of PR2 defects, when compared to the proton irradiated baseline sample.
Maximenko, S.*; Lumb, M.*; Hoheisel, R.*; Gonz lez, M.*; Scheiman, D.*; Messenger, S.*; Tibbits, T. N. D.*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; et al.
lez, M.*; Scheiman, D.*; Messenger, S.*; Tibbits, T. N. D.*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; et al.
Proceedings of 40th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-40) (CD-ROM), p.2144 - 2148, 2014/06
In this paper, a complex analysis of the radiation response of GaAs solar cells with multi quantum wells (MQW) incorporated in the i-region of the device is presented. Electronic transport properties of the MQW i-region were assessed experimentally by the electron beam induced current (EBIC) technique. A 2-D EBIC diffusion model was applied to simulate EBIC line scans across device structure for different radiation doses. The results are interpreted using numerical modeling of the electrical field distribution at different radiation levels. Type conversion from n- to p-type was found in MQW i-region at displacement damage dose as low as low as 1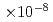 MeV MeV/g. This is supported by experimental and simulated EBIC and electric field distribution results.
MeV MeV/g. This is supported by experimental and simulated EBIC and electric field distribution results.
Furuya, Kazuyuki; Wakai, Eiichi; Miyamoto, Kenji*; Akiba, Masato; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(1), p.494 - 499, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A partial mock-up of a breeding blanket structure made of F82H steel has been successfully fabricated. In this study, microstructural observation and EDX analysis of the HIP interfaces were performed, and effects of irradiation on mechanical properties of the HIP-bonded region were also examined. Neutron irradiation was performed up to about 2 dpa at about 523 K. After the irradiation, tensile test was performed at temperatures of 295 and 523 K. The HIP interfaces possessed many precipitates, and enriched peak spectrum of chromium was detected from the precipitates. In addition, aspect of the spectrum was qualitatively equivalent to that of M C
C in grain boundaries of F82H steel. In result, the HIP boundary has many M
in grain boundaries of F82H steel. In result, the HIP boundary has many M C
C which were generally seen in grain boundaries of F82H steel. Rupture did not occur in the HIP interface. In result, it can be mentioned that bondability is maintained under the irradiation and testing conditions. The strength and elongation of the HIP-bonded region decreased somewhat in comparison with the results of an IEA standard steel.
which were generally seen in grain boundaries of F82H steel. Rupture did not occur in the HIP interface. In result, it can be mentioned that bondability is maintained under the irradiation and testing conditions. The strength and elongation of the HIP-bonded region decreased somewhat in comparison with the results of an IEA standard steel.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro*; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobiyama, Mamoru*; Inami, Takashi*; Kambara, Tadashi*; Okuda, Shigeo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.171 - 175, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have studied effects of irradiation with energetic particles on defect accumulation in nanocrystalline gold (nano-Au). The specimens of nano-Au foil (3-5  m thickness) with various grain sizes (23-156 nm) are prepared by the gas deposition method and subsequent thermal annealings. Irradiations of the specimens with 60-MeV
m thickness) with various grain sizes (23-156 nm) are prepared by the gas deposition method and subsequent thermal annealings. Irradiations of the specimens with 60-MeV  C ions, 3.54-GeV
C ions, 3.54-GeV  Xe ions or 2.0-MeV electrons are performed at low temperature. The defect accumulation behavior is observed by measuring the electrical resistivity change during irradiation. Through an analysis of defect accumulation behavior, cross-sections for defect production,
Xe ions or 2.0-MeV electrons are performed at low temperature. The defect accumulation behavior is observed by measuring the electrical resistivity change during irradiation. Through an analysis of defect accumulation behavior, cross-sections for defect production, 
 , and annihilation,
, and annihilation, 
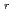 , in nano-Au increase monotonically as the grain size decreases. These results are considered to be caused by the existence of a large volume fraction of the regions near grain boundaries in nano-Au where the threshold energy for atomic displacements, E
, in nano-Au increase monotonically as the grain size decreases. These results are considered to be caused by the existence of a large volume fraction of the regions near grain boundaries in nano-Au where the threshold energy for atomic displacements, E , becomes lower than in polycrystalline gold. The possibility of electronic excitation effects in nano-Au is also discussed.
, becomes lower than in polycrystalline gold. The possibility of electronic excitation effects in nano-Au is also discussed.
Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Takagaki, Masafumi*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ono, Fumihisa*; Neumann, R.*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.161 - 165, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have performed swift heavy ion irradiations in Fe-50at.%Rh alloys at room temperature. Before and after the irradiations, the magnetic properties and the lattice structure are measured using Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) and X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD), respectively. We have also performed X-ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism (XMCD) measurement near the Fe K-edge at the synchrotron radiation facility, SPring-8, to examine the irradiation-induced ferromagnetic state near the specimen surface. We have found that the swift heavy ion irradiations induce the ferromagnetic state in Fe-50at.%Rh alloy below the antiferromagnetism-ferromagnetism transition temperature of the unirradiated alloy and the lattice expasion by 0.3%. For the specimens irradiated with swift heavy ions, we observe the XMCD spectra correponding to ferromagnetisim, which depend on the mass of irradiating ions and/or irradiation fluence. Effects of energy loss through electronic excitation and elastic collisions on lattice and magnetic structures of Fe-Rh alloy are discussed.
Iwase, Akihiro*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Nakatani, Rikizo*; Kato, Yuzaburo*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Baba, Yuji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.141 - 144, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Diffusion of Si atoms in Pd under energetic ion irradiation is studied in Pd-Si thin layer system using synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy. Specimens are prepared by depositing Pd on Si single crystals. The Pd layer thicknesses are 10-300 nm. Before irradiation, we observe photoemission spectra only for Pd, but do not find any trace of Si. After irradiation with 3-MeV Si ions, 1-MeV O ions or 200-MeV Xe ions, we observe an additional photoemission component at the binding energy about 3 eV higher than that of Si 1s bulk component. The experimental result implies that the energetic ion-irradiation induces the diffusion of Si atoms from the Si-Pd interface to the Pd layer surface. The shift of the binding energy from the value for the Si bulk can be interpreted as arising from electron charge transfer from Si to Pd. The dependences of photoemission spectra and ion-irradiation induced diffusion on ion-species and ion-fluence are discussed.